CLASSIFICATION OF O-ANTIGENS BASED ON THEIR INITIAL SUGARS:
For the first time a detailed
classification of the individual O-antigens based on the initiating sugar and glycosyl transferase has been shown:
Salmonella is a genus of Gram-negative, flagellated, facultatively anaerobic bacilli of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The major antigenic structures of Salmonella include the lipopolysaccharides (LPS) or the O-antigens and flagellins or the H-antigens. There are 47 O-antigens and 114 H-antigens, which give rise to over 2500 serovars as described in the Kauffmann-White Le Minor scheme.
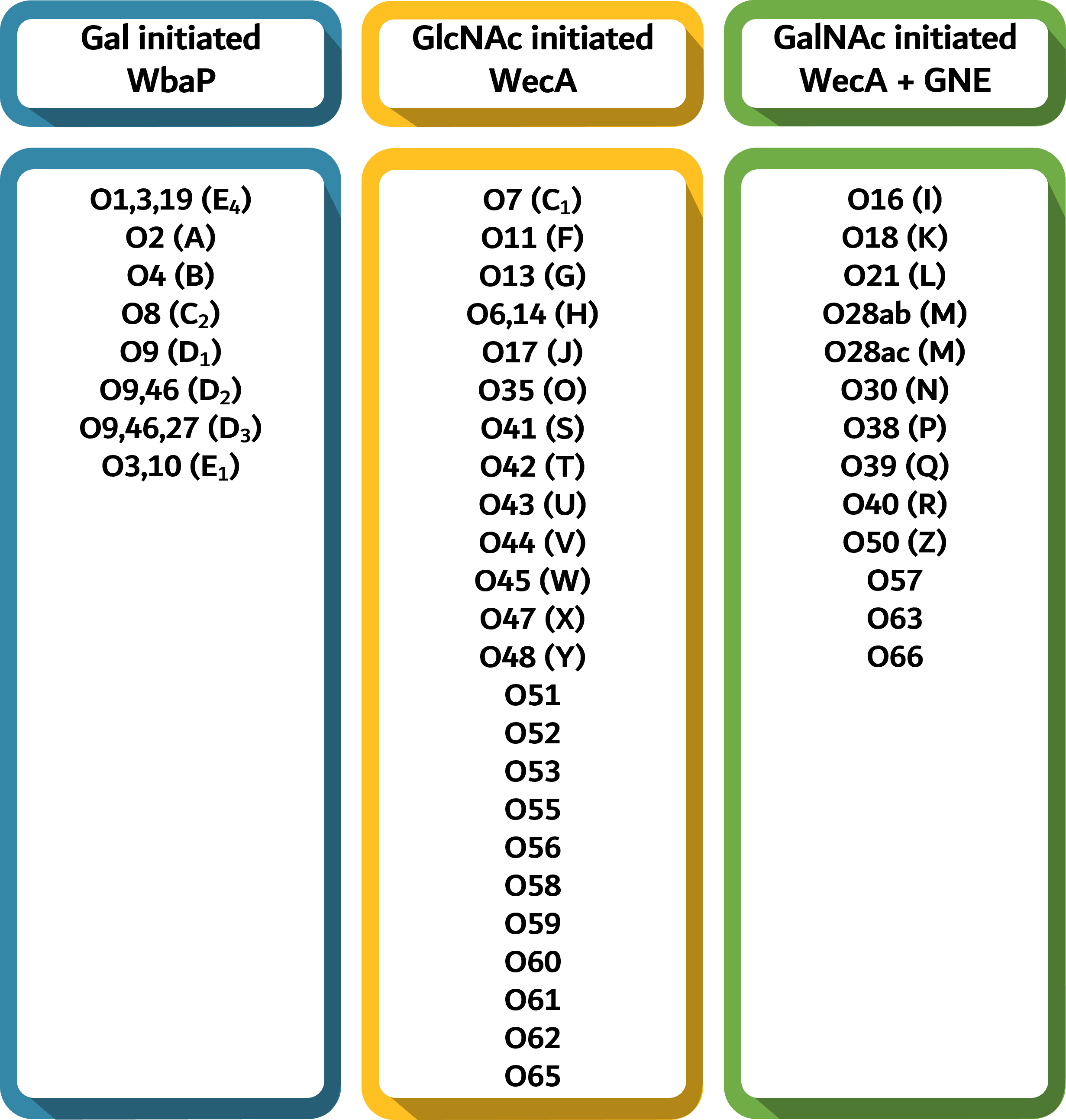
O-antigens can be broadly classified into two major groups based on the first sugar present in the O-unit, namely; Galactose (Gal) OR N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)/N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc).
The biosynthesis of the O-antigen begins with an initiating transferase that falls into two families:
When Gal is the first sugar present in the O-unit, the initiating transferase is WbaP, and if GlcNAc/GalNAc is the first sugar, the initiating transferase is WecA. In the O-antigens with GalNAc as the first sugar, an epimerase encoded by the gene gne converts UndPP-GlcNAc to UndPP-GalNAC.
CLASSIFICATION OF O-ANTIGENS BASED ON THEIR INITIAL SUGARS:
For the first time a detailed
classification of the individual O-antigens based on the initiating sugar and glycosyl transferase has been shown:

Out of the 47 O-antigens, 45 are synthesized by the Wzx/Wzy-dependent pathway and can be distinguished with the help of wzx/Wzx and wzy/Wzy alone and with the support of additional genes to accurately differentiate between a few O-antigens. O54 and O67 and synthesized by the synthase-dependent pathway and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter pathway respectively, and hence lack both wzx/Wzx and wzy/Wzy.
For a few of the O-antigens that couldn't be distinguished accurately with the help of wzx/Wzx and wzy/Wzy alone, additional genes have been incorporated for accurate prediction [rfbE (O2; O9; O9,46); orf17.4 (O3,10; O1,3,19); wecB, wbbE, wbbF (O54); wzm, wzt (O67)] along with 150 glycosyl tranferases.
Unlike O-antigens, H-antigens have highly similar flagellar genes that code for the biphasic H-antigens. The H1 antigen is coded by the flic/FliC and the H2 antigen is coded by the fljb/FljB. Due to their high sequence identity, some of the H-antigens require patterns to distinguish between them. A total of 61 H-antigen sequence patterns have been used to distinguished H-types in addition to the BLAST hit in order to predict the H-antigen accurately.
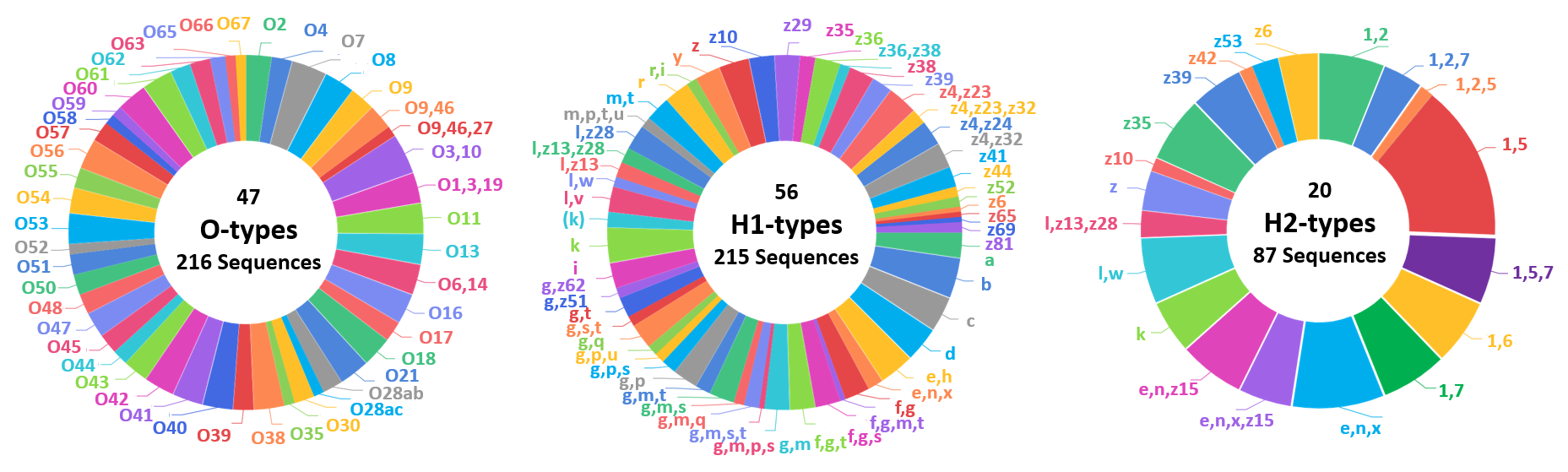
CREATION OF LOCAL DATABASE:
A local database comprising of the reference sequences used for the serotype prediction was created. The following pie chart represents the statistics of the reference sequences used.
PERCENTAGE IDENTITY MATRIX:
The sequence diversity indicated by the percentage
identity matrices revealed that the majority of the O-types can be
differentiated based on Wzx and Wzy alone. Following are the links to the percentage identity matrices.
Wzx
Wzy
Serotype Prediction
SSP accepts the user to input either a protein or nucleotide [Step 1] as their query sequence in the form an NCBI GenBank accession ID [Step 2 (A)], or paste the sequence directly in FASTA format in the given box [Step 2 (B)], or upload a file containing the fasta sequences [Step 2 (C)]. Here is an example of the serotype prediction form. If you would like to submit your own sequence for serotype prediction, visit the Serotype Predictor page.
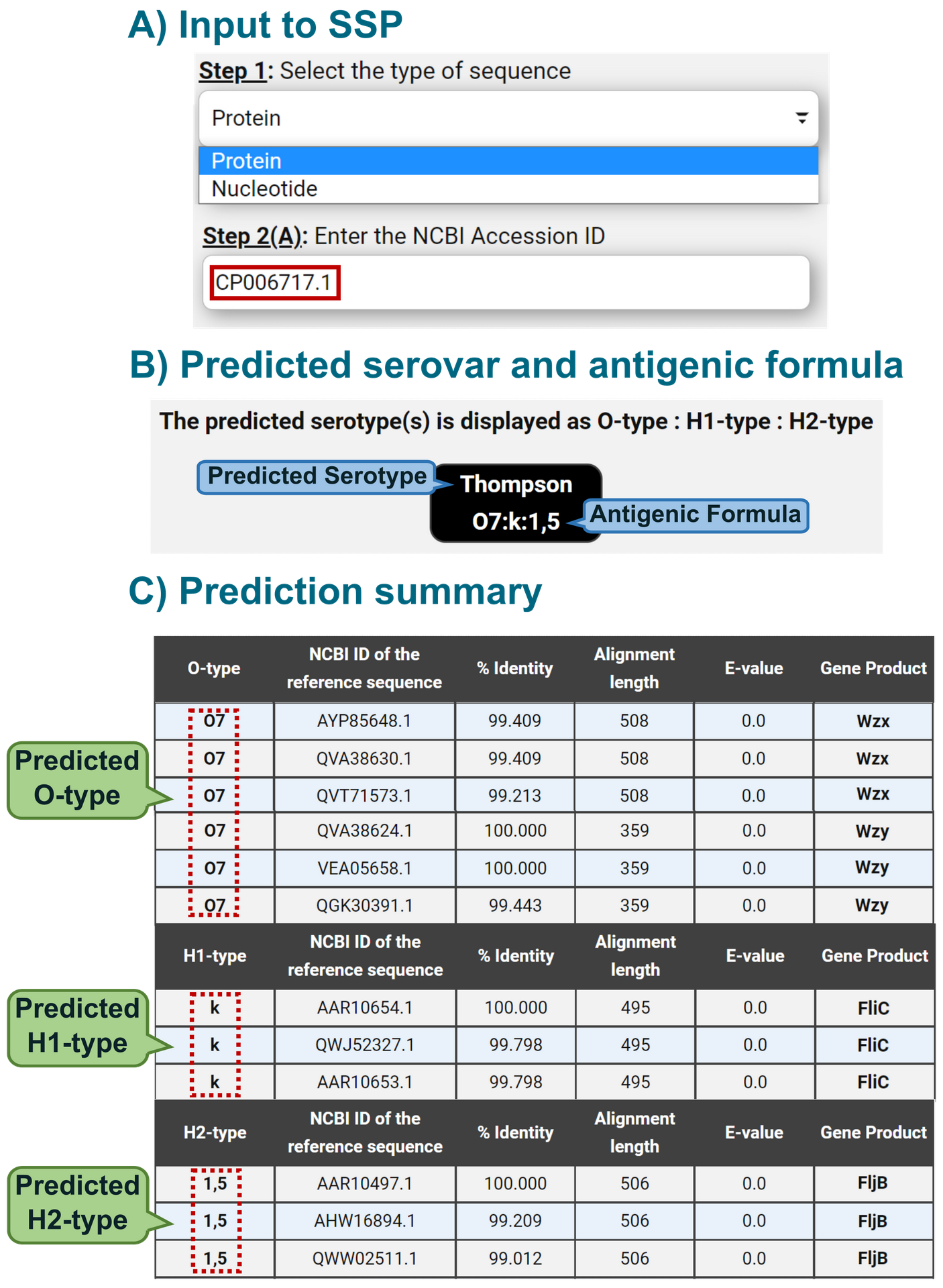
Here's an example of a protein sequence ID being submitted as the input for serotype prediction and an example of what the output page would look like after the prediction of the serotype.
Job ID